Of the birds that we wanted to see in Brazil, this one, the Red-legged Seriema proved the most difficult. Like the Greater Rhea (#598), this is mainly a bird of dry, grassy habitats such as the Cerrado rather than the flood-prone Pantanal. So we hoped to find it at our last lodge, Piuval Lodge in the northern end of the Pantanal just south of Poconé. Even there, we resorted to the help of a local guide, attached to the Lodge, who found one within five minutes of departing from the Lodge. This was the only one we saw, despite further trips through the reserve there.
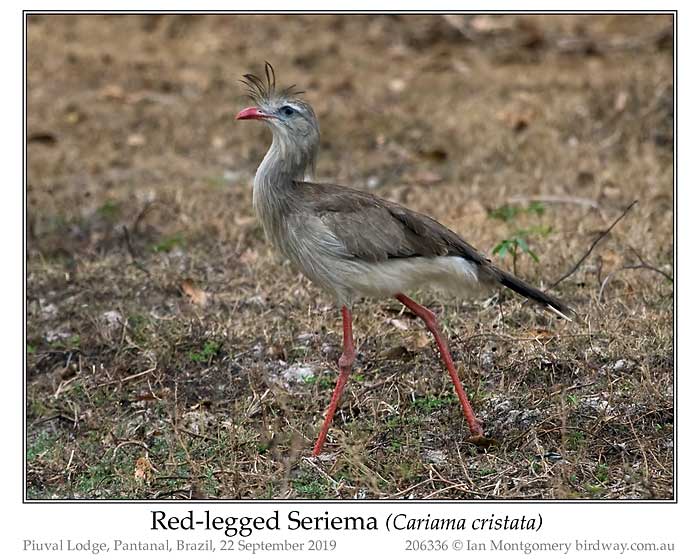

Seriemas are unusual birds. There are only two remaining species, this one and the Black-legged Seriema (Chunga burmeisteri) South American, remnants apparently of a much larger clan known from a few fossils. The Red-legged has quite a wide range through Brazil south of the Amazon basin, Paraguay, eastern Bolivia, eastern Uruguay and north-eastern Argentina. The range of the Black-legged partially overlaps that of the Red-legged but maiinly farther west, still east of the Andes, from southern Bolivia through western Paraguay to central northern Argentina. Despite their remnant status, both are reasonably common in suitable open habitat and classified as of 'Least Concern'.
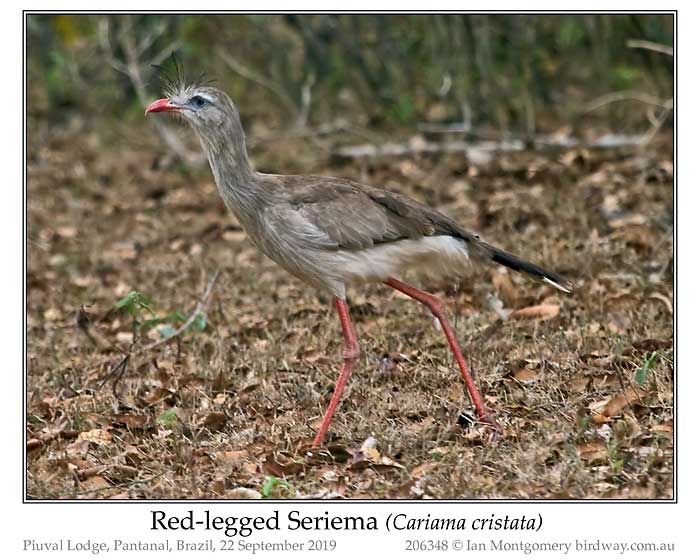

The Red-legged is the larger species, with a length of 75-90cm and weighing 1.5-2.3kg. Both are mainly terrestrial, though they are capable of short bursts of flight, and will often perch in bushes and small trees, where they build their nests. Both species are predatory, feeding on small reptiles such as snakes and lizards, and large insects, but will also feed on seeds. Both are very vocal and join in the morning chorus, though we had listened in vain for the distinctive song of the Red-legged. This is a 'calm series of nasal, well-separated, and accentuated "hah-hah" notes, lilting up and then down again', according to Ber van Perlo in his Birds of Brazil, though the recording in his app sounds like a very distressed and lonely puppy, and 'calm' is not an adjective I'd have chosen.
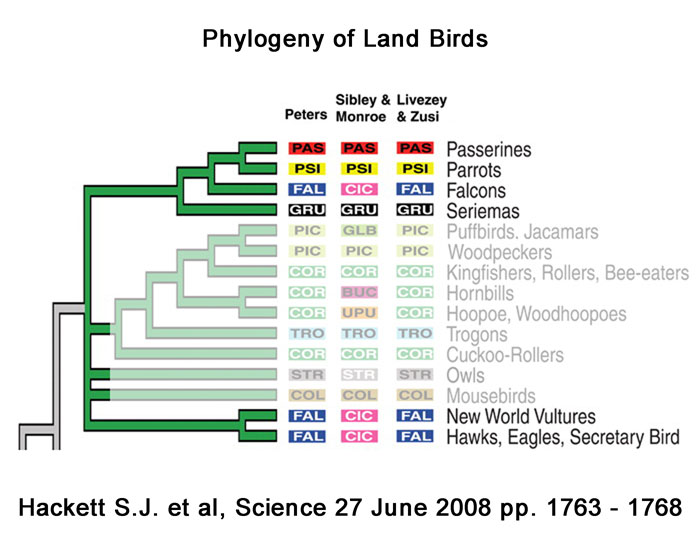
Perhaps most strikingly, the Parrots were shown to be a sister clade to the Passerines, or perching birds, and the Falcons and Caracaras were separated from the other diurnal predators, such as Hawks, Eagles and Vultures. I've highlighted the relevant relationships in the diagram above. Interestingly the Seriemas were an early offshoot of the group that gave rise to the Falcons, Parrots and Passerines. Other studies since have supported these findings and the Seriemas have been elevated to their own order the Cariamiformes. The Passerine order contains half of all extant bird species, 5,000 or so out of 10,000, so the Seriemas have great status in the overall scheme of things with an order to themselves.
Naturally, as you've guessed by now, one of the reasons I was keen to see and photograph it was to fill a taxonomic hole in the species on the Birdway website. Until the advent of DNA analysis, the correct placement of the Seriemas was put in the too-hard basket, which in those days for land birds was in its own family, Cariamidae, in the Crane order, Gruiformes. Cranes were known to be of an ancient lineage, so Gruiformes was a bit of a taxonomic dumping ground for such problem groups, 'GRU' in the diagram above. That all changed in 2008 with this landmark DNA study by Hackett et al. which revolutionised the understanding of the relationships among major groups of birds.
I couldn't help to see a certain resemblance to Bustards in size, form and habit, but perhaps the Secretarybird of Africa is the closest analogue. I've seen this species in pre-digital days in Zimbabwe but I haven't photographed it, so I've taken the liberty of including this splendid photo by Janelle Morano which is published in the Cornell online Birds of the World and the related Macaulay Library: Secretarybird.
If you return to the Hackett diagram you'll see that the Secretarybird is a relative of the hawks and eagles: it is the sole member of one family - Sagitariidae - of the four that make up the order Accipitriformes, the others being the Cathartidae (new world vultures) the Pandionidae (ospreys) and Accipitridae (all the other hawks and eagles). Given the similarities and the relationships to different groups of diurnal predators, the Seriemas and Secretarybird would seem to be a very elegant example of convergent evolution.
So far, I've resisted the temptation of mentioning IT, the current crisis. I will however say that I wasn't intending to be prophetic when I said that the New Year had got off to a bumpy start with the Australian bushfires, and later that the taxonomic puzzle of the Ratites was Gaia's revenge on Homo not so sapiens. Maybe Gaia has turned to self-defence in the way she knows best. I'm largely isolating at home, given the warnings to older people, so I hope to do more work on the website and have more birds of the moment.
Greetings and stay safe,
Ian
Join the The Irregular Bird Club
Birdway has a free Irregular Bird - formerly Bird of the Moment/Week - Club, enjoyed around the world since 2002 by currently 1000 members. An illustrated article is sent to club members at intervals. The photos are significantly better quality images than those on this web page which are compressed more for faster loading.
The club is a Google Group called Birdway to which only Ian can post. To join the group, enter your email address in the Google box below and click the Join button. This will take you to the Google Group joining page for confirmation. Alternatively, email Ian directly using the Contact link below and he'll gladly do it for you and answer any questions.
Ian also uses the Irregular Bird to keep club members up to date with developments, such as improvements to the website and publication of ebooks. He will not reveal your email address to anyone else nor use it for any other purpose.
Page revised on 25 March 2020
 Hide
Hide




